ENGR 21 Fall 2025
HW 5
Summary
Due Date: Tue, Oct 7 at midnight
What to submit:
- Problem (1): A single Python file containing all code for this problem
- Problem (2): A single Python file containing the required function definitions with correct names.
- Problem (3): A single Python file containing the required function definitions with correct names.
- Problem (4) Two
*.pngfiles and two corresponding*.pyfiles that, when run, reproduce the respective plots usingmatplotlib.pyplot.show()
Submit at: This link
(1) Complete in-class activity: Numpy functions
For each of the functions from the numpy package named below, write a line or set of lines of code that demonstrates how this function is used. You must also write a plain-language comment before demonstrating each function, and in this comment you should write what that function does.
The list of functions is:
numpy.array()
numpy.zeros()
numpy.ones()
numpy.empty()
numpy.arange()
numpy.linspace()
numpy.random.rand()
numpy.random.randint()
numpy.reshape()
numpy.transpose()
numpy.concatenate()
numpy.flatten()
numpy.resize()
numpy.shape()
numpy.savetxt()
numpy.loadtxt()
(2) Working with Numpy arrays: Iteration
For each task below, you should create a function that takes as input an arbitrarily-sized 2D array. The functions need not return anything. The functions should be named as func2_1(...), func2_2(...), func2_3(...), where the number after func2_ denotes the part number in the following list.
You may wish to test out your code on arrays of arbitrary size. Initialize random arrays of specified size using the syntax
numpy.random.randint(1,10,size=(7,10))
This will create a $7 \times 10$ array of integers between 1 and 10.
- The
numpy.arraytype is iterable, just likelists andtuples are. Use this fact to write aforloop that iterates over the array that you created and prints all the rows. - The function
numpy.nditercreates a different type of iterable when applied to an object of typenumpy.array. Use this fact to write aforloop that iterates overnumpy.nditer(your array), and prints all the elements. - It is also possible to iterate over
numpyarrays using the familiarfor x in range(n)technique. Use a nestedforloop (i.e., a total of two loops, one inside the other) to print every element in the array. It should first print out all the elements of the first row, starting from the first column (i.e., starting from the left), then all the elements of the second ~column~ row [typo corrected on Oct 22], and so on. - Repeat 3, but this time, your function should print out the first column first, starting from the top; then it should move to the next column, and so on.
(3) Working with Numpy arrays: Manipulating arrays
For this problem, please name your functions func3_1, func3_2, and func3_3.
-
Write a function that reverses the order of rows in a
numpyarray. The function should take an arbitarily-sized 2D array and return a 2D array of the same size. -
Write a function that reverses the order of columns in a
numpyarray. The function should take an arbitrarily-sized 2D array and return a 2D array of the same size. -
Write a function that takes as input argument a square 2D array, i.e. with shape
(n,n)and returns as output a 1-dimensionalnumpyarray of lengthncontaining the diagonal elements of the 2D array.
(4) Plotting
Plotting Mathematical functions in matplotlib
Your goal in this task is to reproduce the following figure as closely as possible.
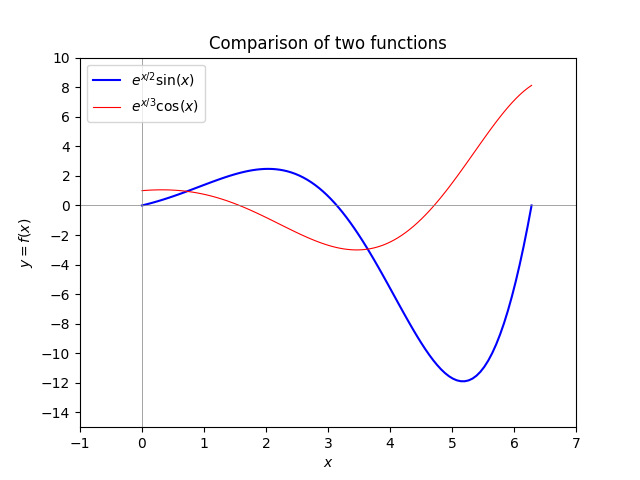
You will turn in both a *.png file and a Python script (i.e., a *.py file that, when run, reproduces your image). Your figure should satisfy the following criteria:
Plot the two functions \(y = e^{x/2} \sin x\) and \(y = e^{x/3} \cos x\)
over the range $x \in [0,2\pi]$.
- The y-axis range should be from -15 to 10.
- The y-axis should have tick marks at even numbers.
- The x-axis range should be from -1 to 7.
- The x-axis should have tick marks at integer intervals.
- There should be light-gray axes inside the figure, i.e. straight lines at $x=0$ and $y = 0$. These lines should have a width that is less than the width of the lines depictuing the functions.
- The function $e^{x/2}\sin(x)$ should be blue, and the function $e^{x/3}\cos(x)$ should be red.
- There should be a legend as shown.
- The two functions should be listed in the order shown in the legend.
- There should be a title
- There should be labels for the horizontal and vertical axes.
- The PNG file should be produced programmatically; you cannot just screenshot the plot.* Your Python script should include
importcommands at the top formatplotlib.pyplotas well asnumpy.
Plotting numerical data using matplotlib
Download this data file, which contains the data necessary to reproduce the following plot. Write a script in Python, making use of matplotlib.pyplot, that generates the following plot.
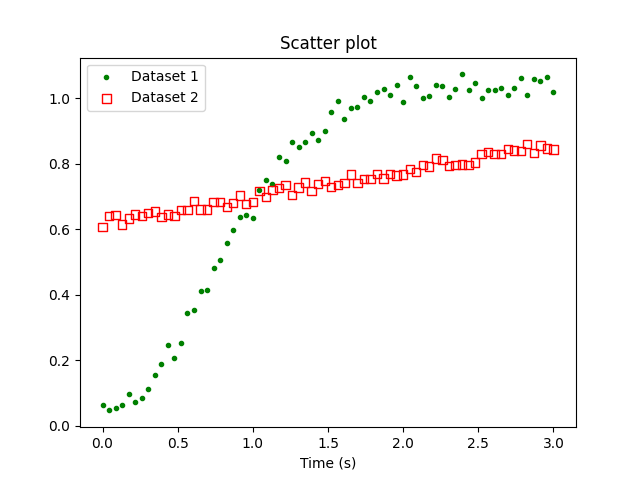
As above, you should reproduce as many features of the above plot as you can. In particular, the color and style of the markers should closely match the above figure.