ENGR 21 Fall 2025
HW 8 Solutions
- HW 8 Solutions
(1) LU Decomposition
(2) Gauss-Seidel Method: an iterative approach to solving $Ax=b$
from numpy import dot
from numpy.linalg import norm
def GaussSeidelv1(A,b,x0,tol=1e-6):
x = x0.copy() # best to work on a "copy"
n = len(A)
while True:
for i in range(n): # i is the row number
x[i] = b[i]/A[i,i] # not done yet! we'll keep updating
for j in range(n):
if i != j:
x[i] -= (A[i,j]*x[j])/A[i,i]
r = b - dot(A,x) # residual
if norm(r) < tol:
break
return x
(3) Gradient-based methods
1) Compare number of steps
from numpy import dot, loadtxt, zeros
from numpy.linalg import norm
from numpy import transpose as tr
def GaussSeidelv2(A,b,x0,tol=1e-6):
x = x0.copy() # best to work on a "copy"
n = len(A)
numSteps = 0
while True:
numSteps += 1
for i in range(n): # i is the row number
x[i] = b[i]/A[i,i] # not done yet! we'll keep updating
for j in range(n):
if i != j:
x[i] -= (A[i,j]*x[j])/A[i,i]
r = b - dot(A,x) # residual
# print("Done with one step. Res = ",norm(r))
if norm(r) < tol:
break
print(f"Gauss-Siedel took {numSteps} steps")
return x
def conjugate_gradientv2(A,b,x_guess,tol=1e-6):
# Uses the conjugate gradient method to solve Ax=b within tolerance specified by 'tol'.
x = x_guess.copy()
r = b - dot(A,x)
beta = 0
s = r.copy()
numSteps = 0
while 2+2 == 4:
numSteps += 1
a = dot(tr(s),r)/(dot(dot(tr(s),A),s)) # step size alpha
x = x + a*s # update x
r = b - dot(A,x) # calculate residual
if norm(r) < tol:
break
beta = - (dot(dot(tr(r),A),s)/
(dot(dot(tr(s),A),s))) # step size beta
s = r + beta*s # update search direction
print(f"Conjugate Gradient took {numSteps} steps")
return x
# Test on given problem
A = loadtxt('test_A.txt')
b = loadtxt('test_B.txt')
# Start Gauss-Seidel with a guess of zeros
GaussSeidelv2(A,b,zeros(len(b)))
# Start Conjugate Gradient with a guess of zeros
conjugate_gradientv2(A,b,zeros(len(b)))
The output of the above program is:
Gauss-Siedel took 39 steps
Conjugate Gradient took 15 steps
2) Modify code so that the norm of the residual is reported
from numpy import dot, loadtxt, zeros, trim_zeros
from numpy.linalg import norm
from numpy import transpose as tr
def GaussSeidelv3(A,b,x0,tol=1e-6):
x = x0.copy() # best to work on a "copy"
n = len(A)
numSteps = 0
norm_residuals = zeros(100) # or some large number.
while True:
numSteps += 1
for i in range(n): # i is the row number
x[i] = b[i]/A[i,i] # not done yet! we'll keep updating
for j in range(n):
if i != j:
x[i] -= (A[i,j]*x[j])/A[i,i]
r = b - dot(A,x) # residual
norm_residuals[numSteps-1] = norm(r)
# print("Done with one step. Res = ",norm(r))
if norm(r) < tol:
# No need to store more numbers, so "trim" the zeros.
trim_zeros(norm_residuals)
break
return x,norm_residuals
def conjugate_gradientv3(A,b,x_guess,tol=1e-6):
# Uses the conjugate gradient method to solve Ax=b within tolerance specified by 'tol'.
x = x_guess.copy()
r = b - dot(A,x)
beta = 0
s = r.copy()
numSteps = 0
norm_residuals = zeros(100)
while 2+2 == 4:
numSteps += 1
a = dot(tr(s),r)/(dot(dot(tr(s),A),s)) # step size alpha
x = x + a*s # update x
r = b - dot(A,x) # calculate residual
norm_residuals[numSteps-1] = norm(r)
if norm(r) < tol:
# No need to store more numbers, so "trim" the zeros.
trim_zeros(norm_residuals)
break
beta = - (dot(dot(tr(r),A),s)/
(dot(dot(tr(s),A),s))) # step size beta
s = r + beta*s # update search direction
return x,norm_residuals
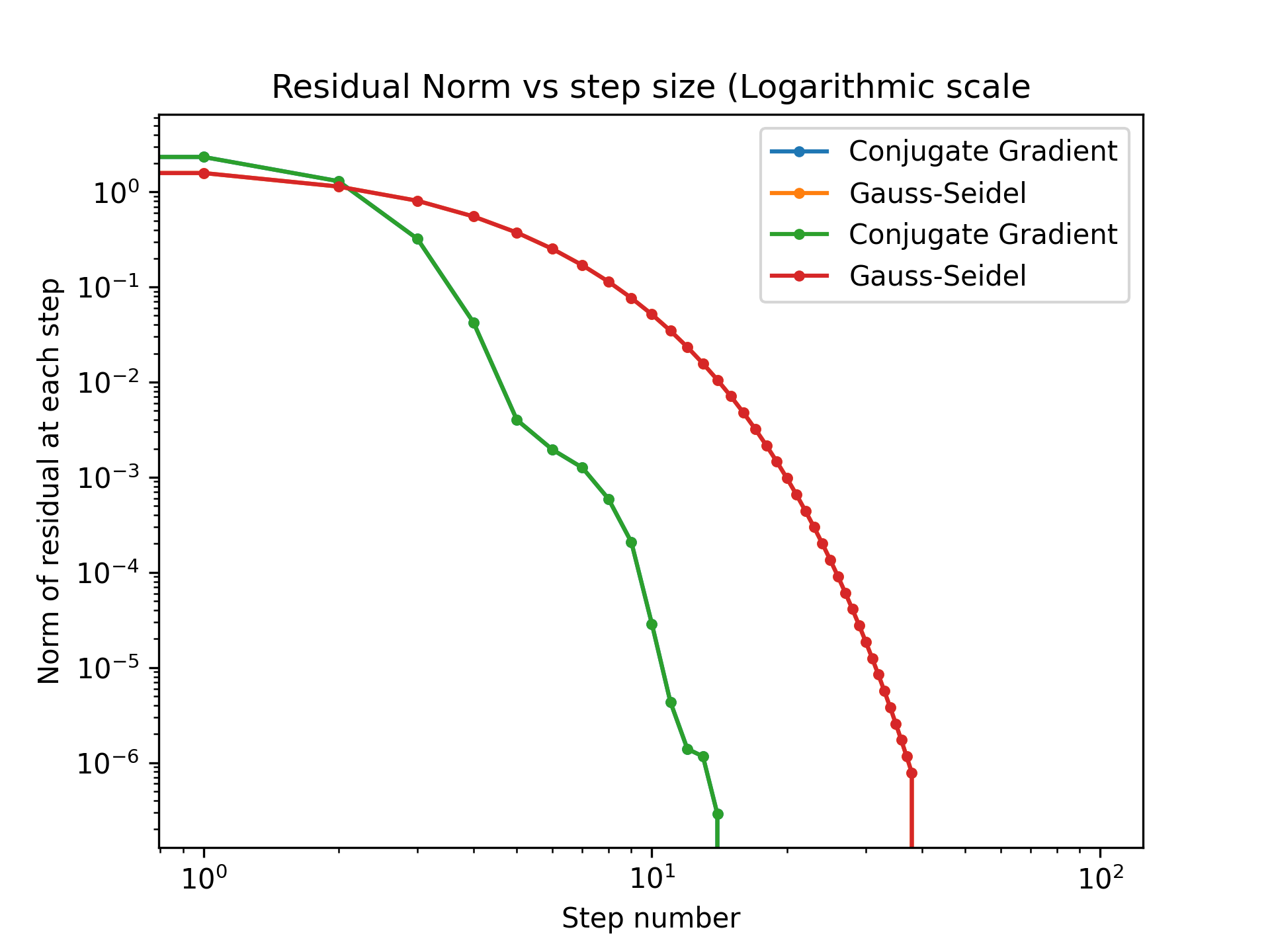
3) Plot the norm of the residual vs. the step number (linear)
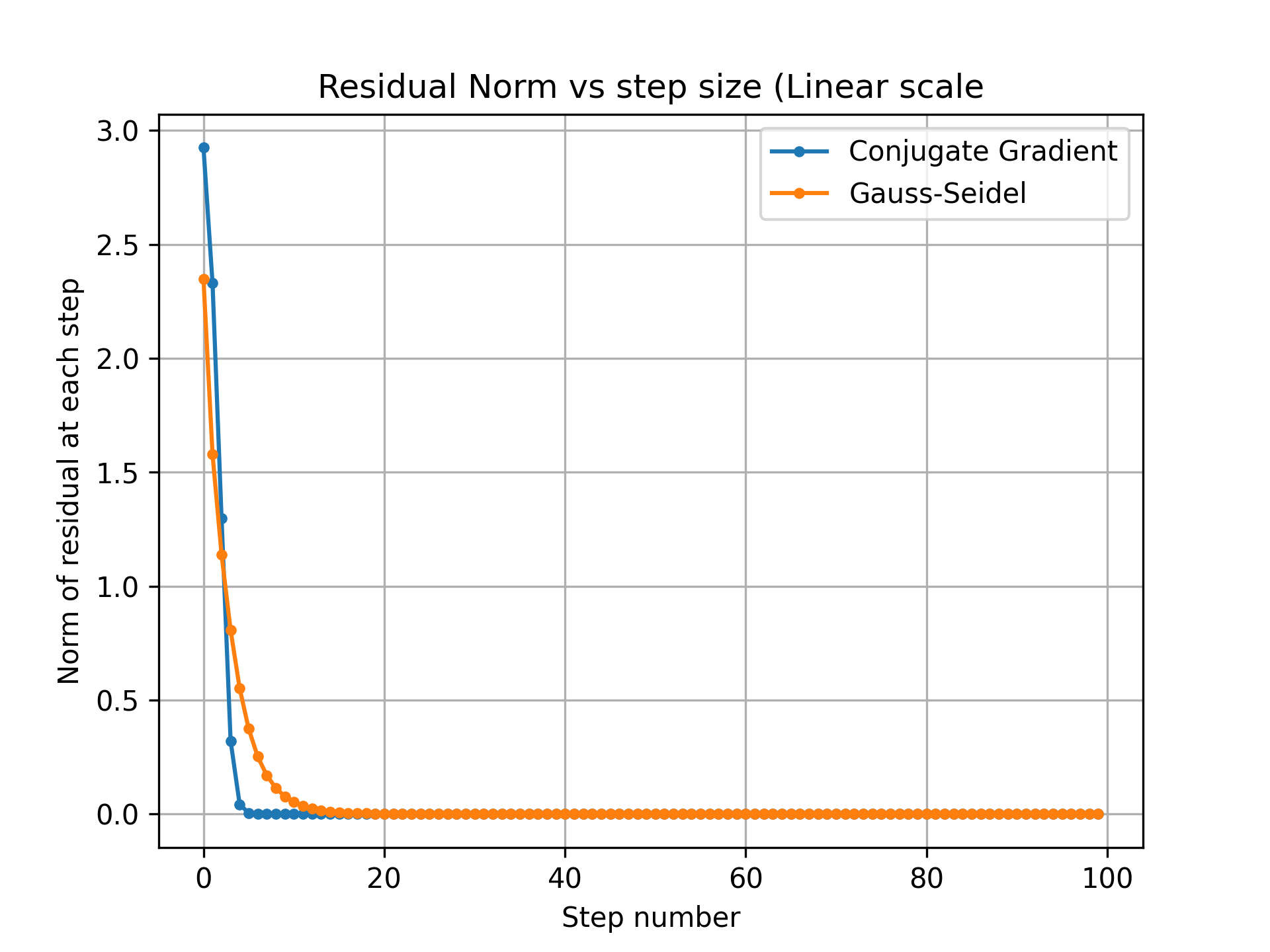
4) Plot the norm of the residual vs. the step numnber (log)